Augmented Reality (AR) is a rising technology in this fast era of modernization. It is no longer just a figment of science fiction imagination or a mere plaything for mobile games. It has burgeoned into a powerful tool, significantly impacting various industries, with construction being one of the most profoundly affected sectors. AR in construction marries the physical world with digital data, providing a composite view that’s enhancing the way buildings are designed, constructed, and maintained.
Main Benefits of Using Augmented Reality in the Construction Industry
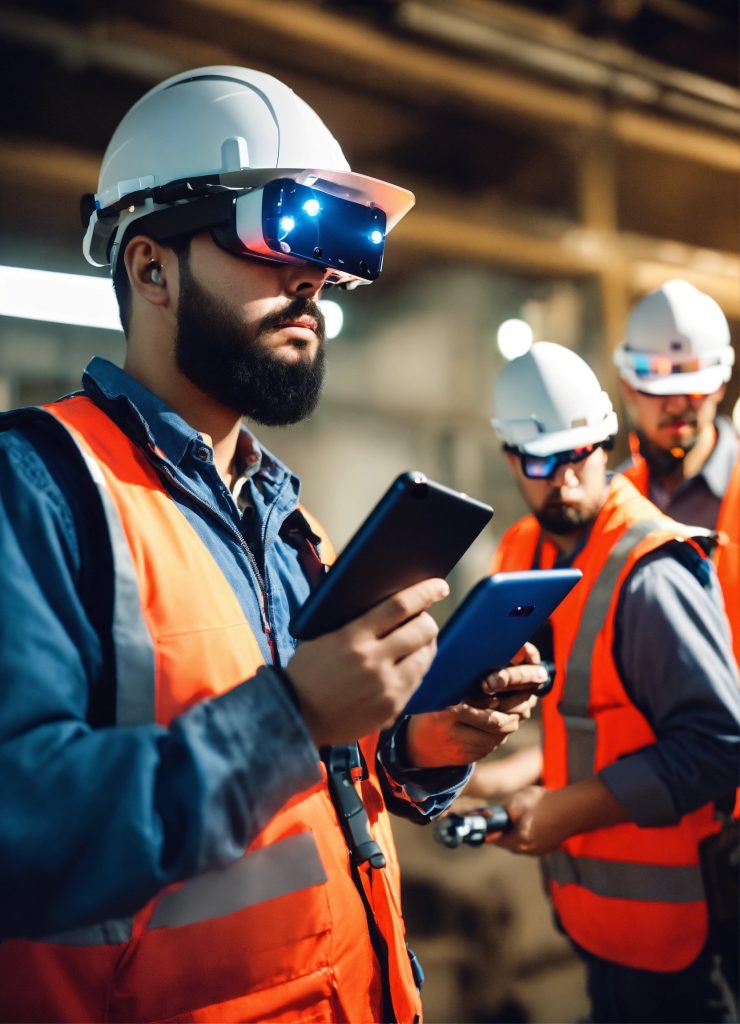

1. Enhanced Visualization
Before the first brick is laid, Augmented reality is the technology that enables architects and clients to visualize the final product. Through AR glasses or mobile devices, stakeholders can walk through the virtual structure, understand spatial relationships, and make necessary adjustments before construction begins, saving both time and money.
2. Improved Accuracy
AR tools can overlay digital plans onto a physical space, allowing for precise measurements. This precision minimizes errors, ensures structures are built correctly the first time, and reduces the need for costly corrections.
3. Efficient Collaboration and Communication
AR facilitates better collaboration among architects, engineers, and construction workers by providing a unified, interactive view of the project. Changes and updates can be made in real-time, ensuring that all parties are always on the same page.
4. Safety Training
AR can simulate construction progress within a controlled environment for training purposes. Workers can practice safety protocols without the risk of real-world accidents, enhancing their preparedness for on-site challenges.
5. Maintenance and Repair
For existing structures, AR can help maintenance teams visualize the building’s internal systems, such as plumbing and electrical, without tearing down walls. This visibility makes maintenance and repair tasks more efficient and less intrusive.
6. Good Project Management
Project managers can use AR to monitor the progress of a construction project against its timeline and budget. By overlaying the project’s digital model over the actual construction site, they can quickly identify discrepancies or delays.
Real-World Examples of Augmented Reality in Construction
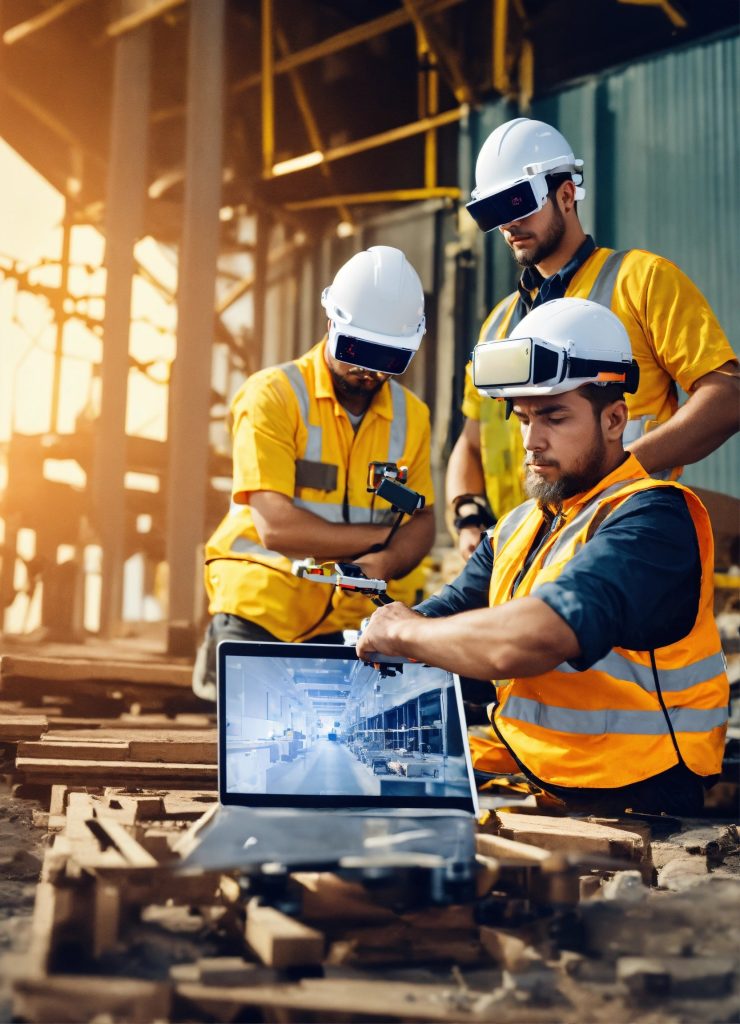

Overlaying BIM Models: Companies are using AR to overlay Building Information Modeling (BIM) data onto the physical construction site, allowing workers to see the digital blueprints in context and adjust their work accordingly.
Remote Assistance: Technicians wearing AR glasses can receive real-time instructions and guidance from experts located elsewhere, enabling them to perform complex installations or repairs without delay.
Training and Safety: Construction firms are implementing AR to conduct safety training sessions, where workers can experience hazardous conditions virtually and learn how to react without any real-world risks.
Historical Restoration: AR is used in historical restoration projects to visualize the original appearance of old or damaged structures, aiding in accurate restoration efforts.
If you are interested to read about 3d printing technology, click here.
If you are interested to read about self-healing concrete, click here.
FAQ’s about AR in Construction
Q1: Is Augmented Reality in construction expensive?
A1: While initial setup costs can be significant, the return on investment through reduced errors, improved efficiency, and better project management often outweighs the expense.
Q2: Can Augmented Reality (AR) be used in small-scale construction projects?
A2: Absolutely, Augmented Reality (AR) technology is scalable and can be adapted for projects of any size, offering benefits from enhanced visualization to improved accuracy even in smaller ventures.
Q3: Do construction workers need special training to use AR?
A3: Yes, but the training is straightforward. Familiarity with AR devices and software is necessary, but most systems are designed for ease of use.
Q4: How does AR improve project management?
A4: AR provides project managers with a real-time, interactive view of the project’s progress, allowing for immediate adjustments and better resource allocation.
Q5: What are the limitations of AR in construction?
A5: Challenges include dependency on device battery life, the need for robust software that can handle complex data, and ensuring that digital information accurately aligns with the physical site.
Q6: What’s the future of AR in construction?
A6: The future of this technology is, with ongoing advancements likely to make AR even more integrated into daily construction activities. From design and planning to maintenance and inspection, AR’s role in construction is only set to expand.
Final Words
Concluding the discussion, Augmented reality is transforming the construction industry by offering unparalleled benefits in visualization, accuracy, communication, and safety. Its ability to merge digital information with the physical world is not just enhancing the way we build but also paving the way for a future where construction projects are more efficient, safer, and aligned with the evolving needs of our society.