In the world of architecture, parapet walls are important for both functional and aesthetic point of view. These are basically the short walls, extend above the roofline of a building, can be designed in many different ways. They’ve been used in everything from old forts to tall modern buildings, and they’ve changed a lot over time. This blog post discusses about the significance of parapet walls, its functions and designs. The blog highlights their contribution to the visual appeal and structural integrity of buildings.
What is Parapet Wall?
A parapet wall is a low protective barrier or railing typically found at the edge of a roof, balcony, terrace, or bridge. Historically, parapets were primarily used for defensive purposes in fortifications, providing cover for soldiers while defending against enemy attacks. Over time, their functionality expanded beyond defense to include elements of drainage, privacy, and architectural ornamentation.
Types of Parapet Walls
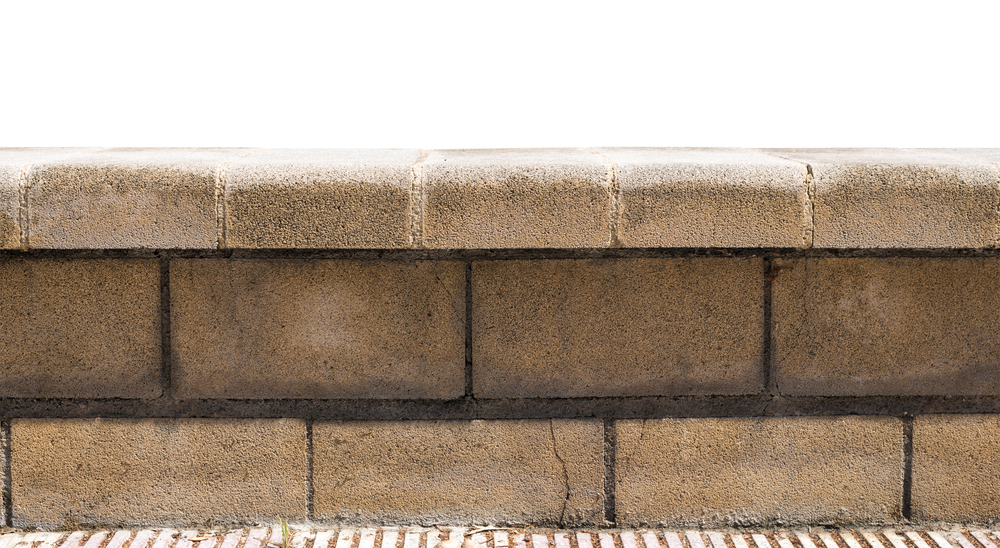

Here are basically 3 categories in which parapet walls are divided.
- By Design Style
- By Shape and Configuration
- By Material
Now, we discuss these categories of parapet walls in details.
1. By Design Style
Plain: The traditional solid parapet wall with simple design
Embattled: Featuring indentations resembling medieval castle crenellations, often seen in historical structures.
Perforated: Incorporating openings and patterns for visual interest, light filtration, or even seating.
Paneled: Featuring decorative panels made from various materials for added style.
2. By Shape
Following are the types of parapet walls classified on the basis of shape
Flat: The most common form, providing a level barrier.
Sloped: Angled upwards for drainage or aesthetic purposes.
Stepped: Featuring multiple tiers, adding visual complexity and potentially offering seating.
Curved: Offering a graceful and unique aesthetic, often used in modern architecture.
3. By Materials
Brick Timelessly elegant and durable, suitable for traditional and contemporary styles.
Concrete Precast panels offer a sleek, modern look, often used in commercial buildings.
Metal Perforated metal screens add lightness and transparency, while offering sun protection.
Wood Warm and natural, but requires proper maintenance.
Glass Creates a seamless connection with views, but safety considerations are crucial.
Functions of Parapet Walls
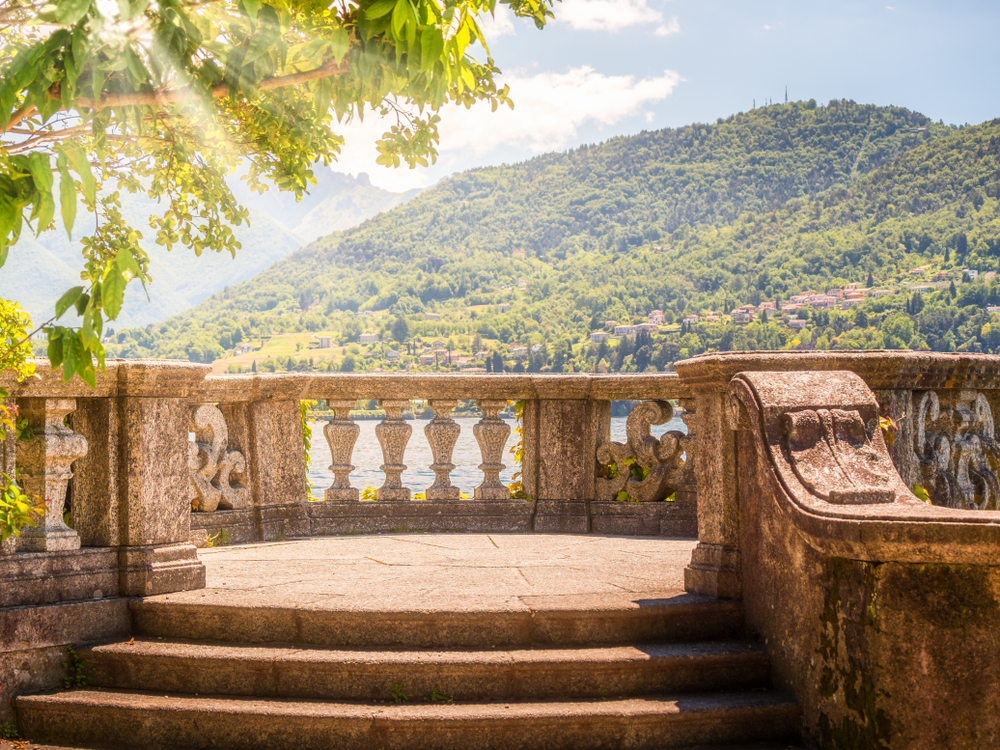

Safety and Protection
One of the primary functions of parapet walls is to provide safety by preventing people from accidentally falling off roofs, balconies, or elevated platforms.
Weather Protection
Parapet walls can shield buildings from wind, rain, and other weather elements, helping to prevent water infiltration and damage to the structure.
Proper Covering
Parapets can conceal rooftop equipment, such as HVAC systems, plumbing vents, and satellite dishes, improving the overall aesthetics of the building.
Architectural Enhancement
Parapet walls contribute to the visual appeal of buildings, adding character, rhythm, and scale to the façade.
Parapet Wall Design Requirements
When designing parapet walls, architects consider various factors such as the building’s function, location, climate, and architectural style. Here are some common design considerations:
Height and Thickness
The height and thickness of a parapet wall depend on its intended function, building code requirements, and aesthetic preferences. Taller parapets provide increased safety and privacy, while thinner profiles can create a sleeker, more modern look.
Materials
Parapet walls can be constructed using a wide range of materials, including brick, stone, concrete, metal, glass, and wood. The choice of material depends on factors such as durability, cost, aesthetics, and structural requirements.
Texture and Finish
The texture and finish of a parapet wall can significantly impact its visual appearance. Smooth finishes exude a contemporary vibe, while textured surfaces add depth and character. Architects may also incorporate decorative elements such as moldings, carvings, or architectural ornamentation to enhance the aesthetic appeal of the parapet.
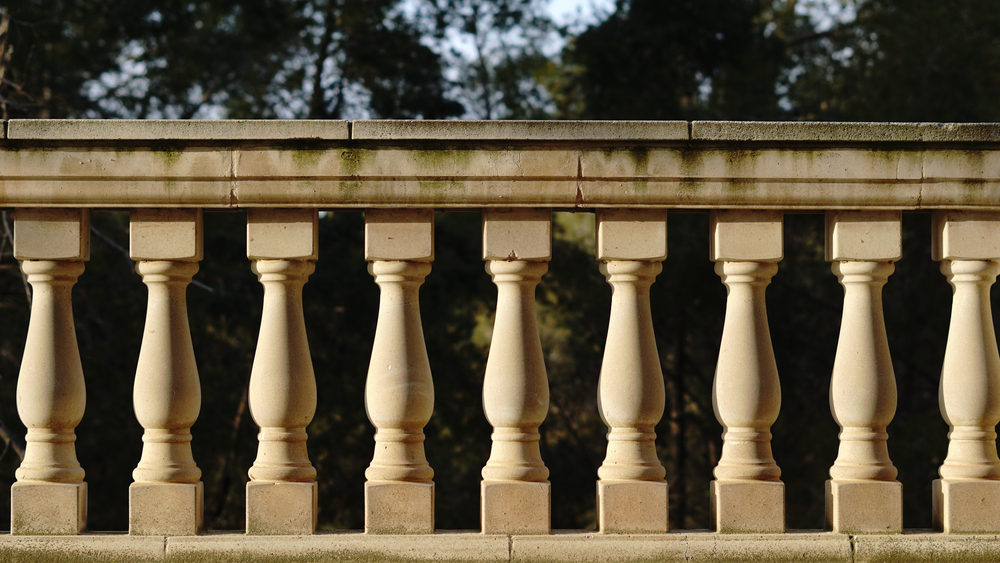
Railing Design
In some cases, parapet walls feature integrated railings or balustrades for additional safety and decorative purposes. The design of these railings can vary widely, ranging from simple metal bars to intricate wrought iron or glass panels.
Decorative Features
Parapet walls offer opportunities for creative expression through decorative features such as cornices, coping stones, finials, and parapet caps. These elements can accentuate the architectural style of the building and add visual interest to the façade.
How to Choose Right Parapet Wall Design

Architectural Theme
Consider the overall architectural style of the building and choose a modern parapet design that complements it.
Material Selection
Consider the multiplefactors including aesthetics, durability, and budget while selecting the parapet wall design materials
Authority Codes Regulation
Ensure the parapet wall design for house meets all the safety regulations and local building codes provided by relevant authorities.
Functionality Focus
Consider if the parapet needs to serve additional purposes like privacy screening or wind deflection.
If you are interested to read about style main gate design of houses in 2024,click here
Conclusion
Parapet walls are important in architecture because they have both practical and decorative purposes. They can act as protective barriers, add visual aesthetics of a building, or make a design statement. By thinking about things like how tall they are, what they’re made of, their texture, and any decorative features, architects can make parapet walls that make buildings look better and create a better experience for people. As architecture evolves, parapet walls will undoubtedly remain integral elements of architectural composition, shaping the skylines and streetscapes of cities around the world.