Architecture, is one of the oldest and most prestigious professions. It is oftenly known as the silent narrator of human civilization. Architecture is not just about designing and mapping of buildings. Infact, it is a beautiful blend of art, science, and usefulness that has evolved over centuries.It is a multidimensional discipline that transcends mere constructions. In this blog article, we examine the fundamentals of architecture, its history, and the core responsibilities of architects that play in influencing the built world.
The History of Architecture
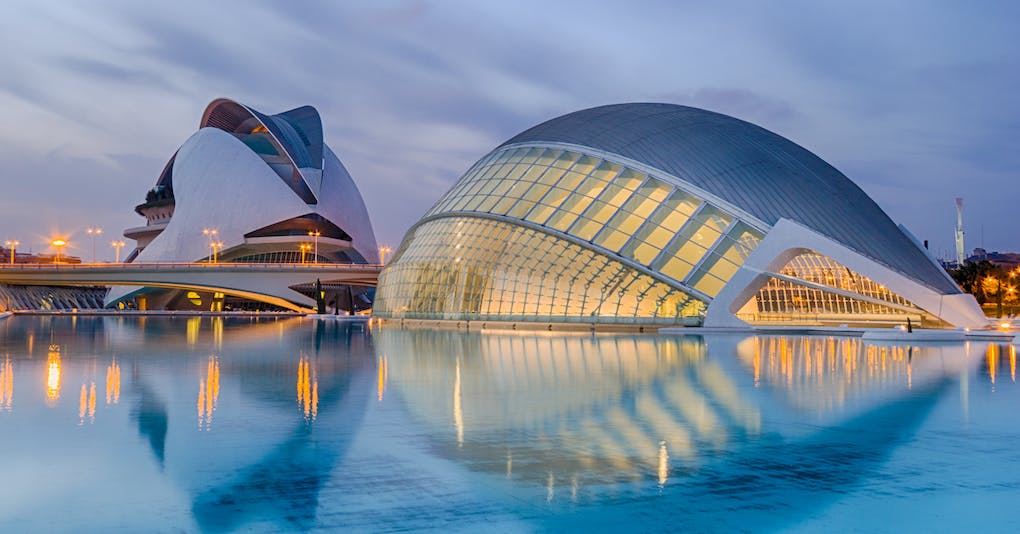

The roots of architecture can be traced back to the dawn of human civilization. From the primitive shelters crafted for survival to the towering structures of today, architecture has mirrored the progression of societies. Ancient civilizations like the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans laid the groundwork for architectural principles, introducing concepts of symmetry, proportion, and durability. The Middle Ages witnessed the emergence of Gothic architecture with its soaring cathedrals, while the Renaissance brought a revival of classical elements and a renewed focus on aesthetics. The industrial revolution marked a pivotal shift, introducing new materials and construction techniques, leading to the birth of modern architecture in the 20th century.
Early Beginnings
- Neolithic Period (c. 10,000 BC): The dawn of architecture with the construction of permanent dwellings and ceremonial structures like Göbekli Tepe in Turkey.
- Ancient Mesopotamia (c. 3500 – 1200 BC): Development of mud-brick architecture, including ziggurats (stepped temples) like the Great Ziggurat of Ur.
- Ancient Egypt (c. 3100 – 332 BC): Monumental stone architecture, including pyramids, temples, and tombs like the Great Pyramid of Giza.
Classical Civilizations
- Ancient Greece (c. 800 – 146 BC): Emphasis on harmony, proportion, and civic spaces. Rise of iconic styles like Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian.
- Ancient Rome (c. 753 BC – 476 AD): Adoption and adaptation of Greek styles, along with advancements in engineering like concrete domes (Pantheon). Development of arches, aqueducts, and urban planning.
Medieval Period
- Byzantine Empire (c. 330 – 1453 AD): Elaborate use of mosaics, gold, and light in churches like Hagia Sophia in Constantinople.
- Islamic Architecture (c. 7th century onwards): Dome and minaret as central elements. Intricate geometric patterns and use of calligraphy in mosques like Alhambra in Spain.
- Romanesque and Gothic Architecture (c. 10th – 15th centuries): Heavy stone construction, vaulted ceilings, and stained glass windows in European churches and cathedrals (Notre Dame).
Renaissance and Beyond
- Renaissance Architecture (c. 14th – 16th centuries): Revival of classical motifs, emphasis on symmetry and beauty in buildings like Palazzo Medici in Florence.
- Baroque and Rococo (c. 17th – 18th centuries): Theatrical and dynamic forms, dramatic light and shadow play, ornate interiors like Château de Versailles.
- Industrial Revolution and Modernism (c. 18th – 20th centuries): New materials like steel and glass, focus on function and simplicity. Architects like Le Corbusier and Frank Lloyd Wright.
Responsibilities of an Architect
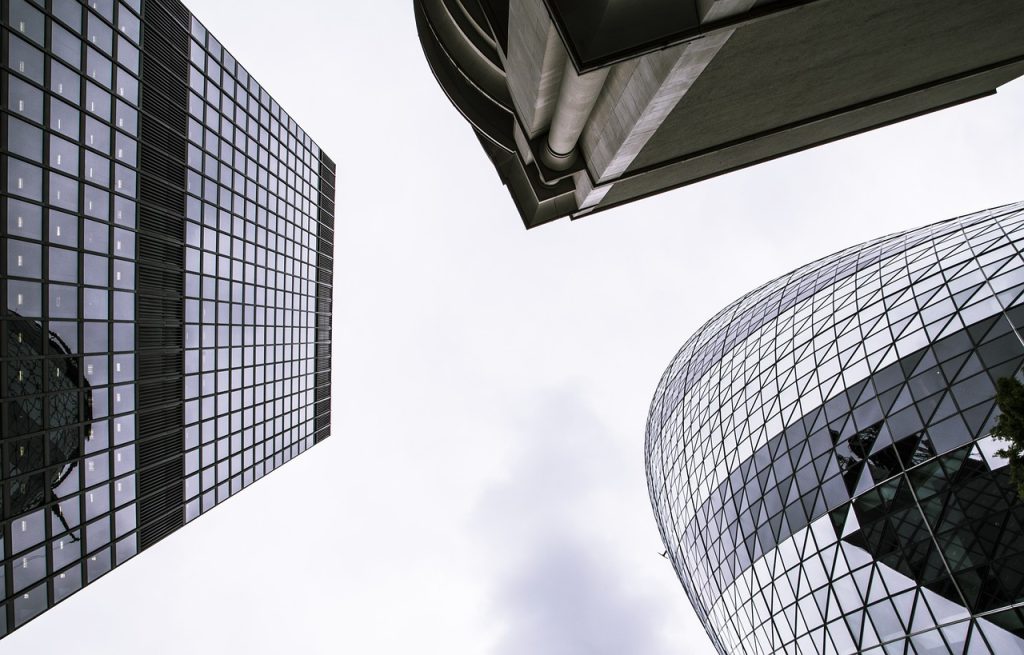

Architects shoulder a bundle of responsibilities. They play a vital role in shaping the physical environment we inhabit. Here are some key responsibilities:
Conceptualization
Architects conceive and develop design concepts, translating ideas into tangible structures that fulfill specific purposes.
Planning
They carefully plan the layout of buildings, considering multiple factors like spatial efficiency, traffic flow, and environmental impact.
Aesthetics
Architects are responsible for creating visually stunning structures that harmonize with their surroundings while reflecting the purpose they are meant to serve.
Technical Expertise
Understanding engineering principles, material science, and construction techniques is vital for architects to ensure the structural integrity and safety of their designs.
Sustainability
Sustainability is an important aspect for construction industry in this modern era. Hence Architects have to focus on creating sustainable designs, minimizing the ecological footprint of buildings.
Regulations and Codes
Compliance with building codes, zoning regulations, and legal requirements is an integral part of an architect’s role to ensure compliance and safety.
Collaboration
Architects collaborate with various stakeholders, including clients, engineers, contractors, and other professionals, fostering effective communication to bring projects to fruition.
Read More:- Top 10 Architects of the World
Read More:- Top 5 Architects of Pakistan
Conclusion
Architecture is an ever-evolving and highly money making field. It is a challenge to human creativity and ingenuity. Architects from all over the world ensure sustainibility and safety of buildings. Thay are the professionals that design aesthetically pleasing structures and decorate our cities and couuntry. The structures around us remain a canvas for architects to showcase their ideas, capturing the essence and dreams of societies across time, both in the past and in the future.