Green Construction is an outstanding innovative idea in the industry of construction. In a world where humans are facing environment polution issues
Green Construction Technology, integrated with Artificial Intelligence (AI), is shaping the future of the construction industry. As the global warming and climate change become more and more apparent, green buildings have become increasingly popular. Green building technology helps to reduce energy consumption and waste, while also reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of green building, the key elements of green construction, and example of a green building, and discuss the fundamental principles behind this sustainable approach. We’ll also provide insightful links to further enhance your understanding of these concepts.
Benefits of Green Building
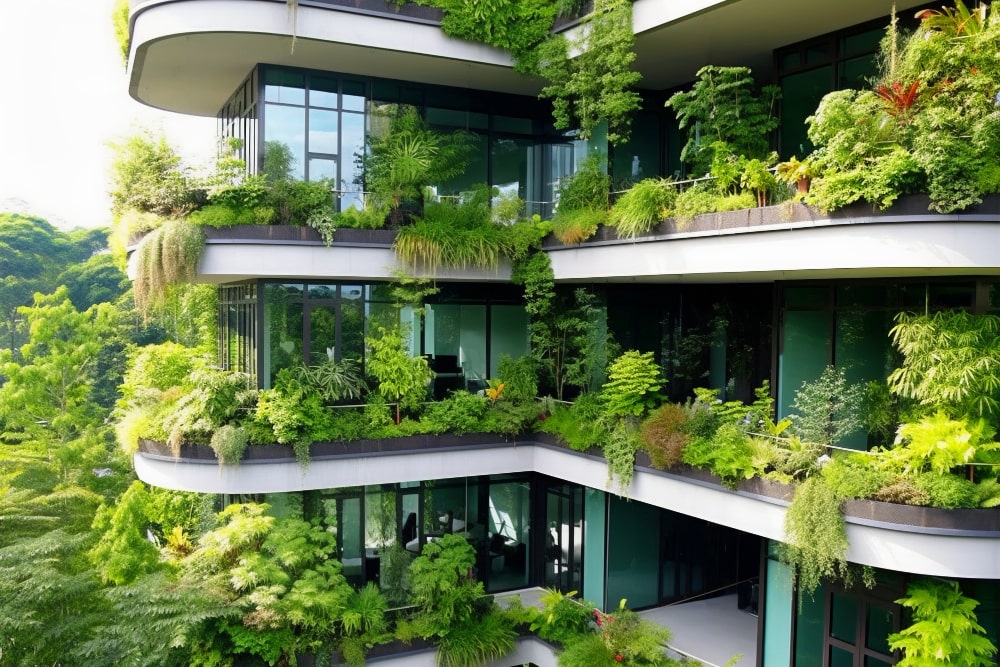

There are many benefits to green building construction, both for the environment and for building owners and occupants.
Eco-Friendly Construction
Green building, often referred to as sustainable or eco-friendly construction, is a design and construction process that focuses on creating structures with minimal environmental impact while ensuring the health and well-being of their occupants. The importance of green building is all due to its eco-friendly nature.
Reduce Environmental Footprint
Green buildings minimize energy and water consumption, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and limit waste generation, thereby reducing their overall environmental footprint. Furthermore, green buildings can also be designed to maximize the use of natural light, reduce air pollution, and promote green transportation.
Enhance Energy Efficiency
Through innovations like AI-driven energy management systems, green buildings use resources more efficiently, resulting in substantial cost savings and a reduced carbon footprint. Green buildings require fewer materials and less energy to build and maintain.
Prioritize Human Health:
Green building design considers indoor air quality, natural lighting, and other factors that contribute to a healthier and more productive living and working environment.
Promote Sustainability
By incorporating renewable materials and construction techniques, green buildings promote sustainable practices that protect natural resources and ecosystems.
The Four Elements of Green Building
Green Building is founded on four core elements, often referred to as the “Four E’s” of sustainability:
Energy Efficiency: Green Buildins aims to optimize the construction process with energy efficiency like AI-based energy management systems.
Environmental Protection: Green construction focuses on reducing the impact of construction on the environment through sustainable practices and materials.
Economic Viability: Balancing sustainable features with cost-effectiveness, demonstrating that green building can be financially advantageous.
Enhanced Health and Well-being: Designing structures that prioritize the well-being of their occupants, from indoor air quality to natural light.
An Example of a Green Building
An iconic example of a green building is the One Angel Square in Manchester, England. This remarkable structure, home to the Co-operative Group, is often hailed as one of the greenest office buildings globally, thanks to its innovative design and AI-integrated systems. Key features of this sustainable building include:
A tri-generation plant that generates power, heating, and cooling more efficiently.
A natural ventilation system that minimizes the need for traditional HVAC.
A striking double-skin façade that regulates temperature and reduces energy consumption.
Rainwater harvesting and a green roof that minimize water usage and support biodiversity.
Principles of Green Building
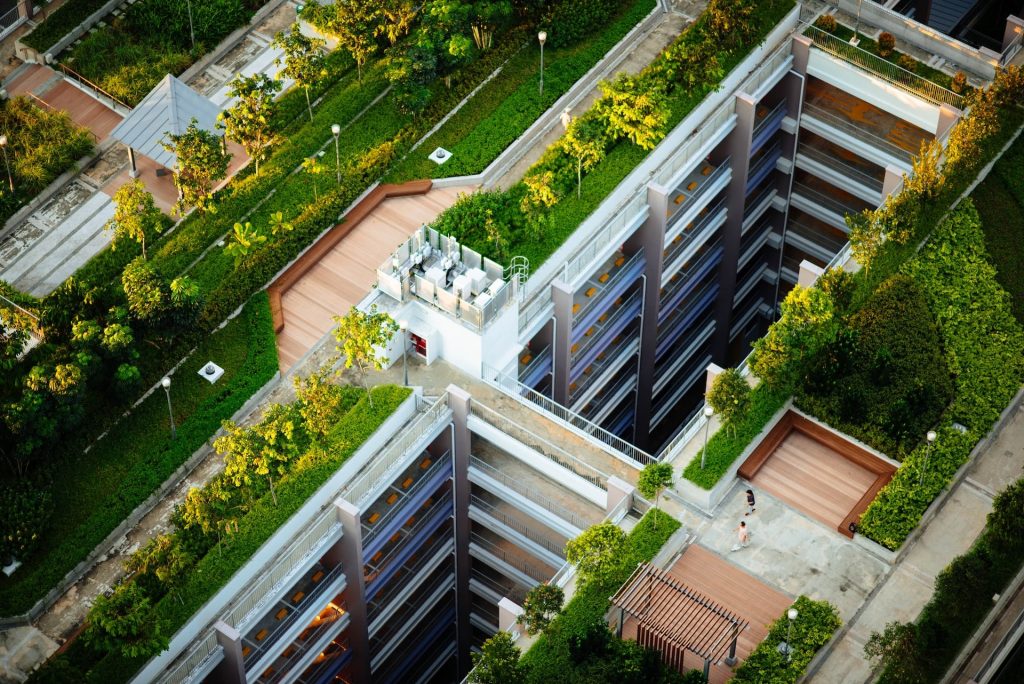

Green building adheres to several fundamental principles that guide its construction:
Sustainable Site Selection: Choosing locations that minimize environmental impact and support efficient land use.
Energy Efficiency: Implementing systems like AI-controlled lighting and HVAC to optimize energy consumption.
Water Efficiency: Reducing water wastage through low-flow fixtures and innovative recycling systems.
Materials Selection: Prioritizing sustainable and locally sourced materials to lower embodied energy.
Indoor Environmental Quality: Focusing on factors like air quality, lighting, and acoustics to improve occupant well-being.
Innovation and Technology: Embracing AI, BIM, and other technological advances to enhance building performance.
Types of Green Buildings
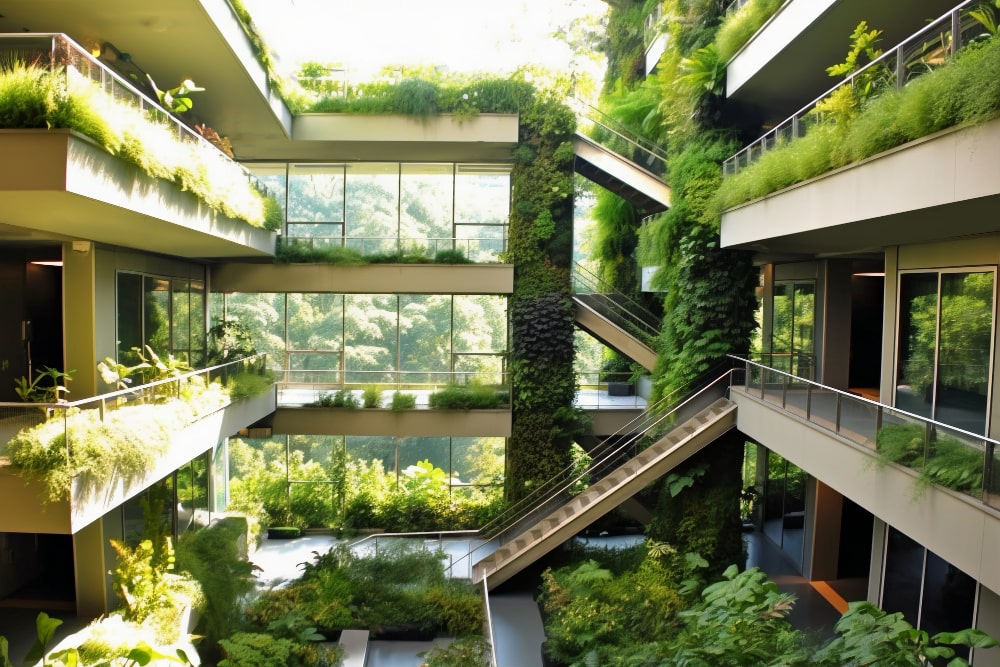

There are different types of green buildings. We enlist few of them as following.
Solar Power Systems
Solar power systems are a cornerstone of green building technology. By harnessing the sun’s energy, photovoltaic panels convert sunlight into electricity, providing a renewable and clean energy source for buildings. Solar panels can be installed on roofs, walls, or as standalone structures. Solar panels require little to no maintenance and have a long lifespan, making them an attractive and cost-effective option for both residential and commercial buildings. Additionally, solar panels can help reduce a building’s carbon footprint.
Energy-Efficient HVAC Systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems play a significant role in a building’s energy consumption. Green building technologies have introduced energy-efficient HVAC systems that optimize temperature control, reduce energy waste, and enhance indoor air quality. Smart thermostats, geothermal heat pumps, and energy recovery ventilators are just a few examples of these eco-friendly innovations.
Green Roofs
Green roofs, also known as living roofs, transform the top of a building into a vibrant ecosystem. They are covered with vegetation, which not only adds aesthetic appeal but also provides insulation, reduces stormwater runoff, and mitigates the urban heat island effect. Green roofs enhance energy efficiency and contribute to cleaner air in urban areas.
Rainwater Harvesting Systems
In a building, rainwater harvesting systems collect and store rainwater for a variety of non-potable uses like irrigation, toilet flushing and washing machines.This technology not only conserves water but also reduces the demand on municipal water supplies, promoting water sustainability and cost savings. Rainwater harvesting systems can help to reduce storm-water runoff, preventing water pollution and flooding.
Smart Building Automation
Smart building automation integrates cutting-edge technology with environmental responsibility. These systems use sensors, AI, and IoT (Internet of Things) to monitor and control a building’s energy usage, lighting, and climate. By adapting to changing conditions and occupancy, smart buildings can significantly reduce energy waste, providing both environmental benefits and cost savings.
Sustainable Building Materials
Sustainable building materials are a vital component of green construction. These materials are eco-friendly, non-toxic, and often feature recycled or renewable content. Examples include bamboo, reclaimed wood, recycled steel, and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) paints. These materials can significantly reduces the environmental impact of construction and enhances indoor air quality. These materials are also cost-effective and can help to reduce construction costs. Additionally, they can be used to create unique, eye-catching designs.
Passive Design Strategies
Passive design strategies aim to maximize a building’s natural resources to reduce energy consumption. This includes optimizing the building’s orientation to capture sunlight and natural ventilation, using thermal mass for temperature regulation, and implementing high-performance windows and insulation.
Net Zero Energy Buildings
A Net Zero Energy Building (NZEB) is a Building that produces as much energy as it consumes over the course of a year. NZEBs are designed to be highly energy-efficient and use renewable energy sources to meet their energy needs. These buildings produce as much energy as they consume, resulting in a net-zero carbon footprint. Achieving this status requires a combination of energy-efficient technologies, on-site renewable energy generation, and smart grid integration. NZEBs are designed to be resilient to extreme weather events and other natural disasters.
Energy-Efficient Lighting
LED lighting technology is a staple of green building, as it offers significant energy savings and a longer lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. Occupancy sensors and daylight harvesting systems further enhance energy efficiency in lighting design. Additionally, the use of natural light through skylights and large windows can reduce the need for artificial lighting. Passive cooling techniques such as shading and insulation can also be employed to reduce energy consumption.
Sustainable Landscaping
The use of native plants and efficient irrigation systems in landscaping helps reduce water consumption and maintain the natural ecosystem. Sustainable landscaping practices create an aesthetically pleasing environment while minimizing environmental impact.
By creating structures that are environmentally responsible, we can reduce our the bad consequences of unhealthy construction practices on earth and contribute to a more sustainable and healthier world for generations to come.
To dive deeper into the world of green building and its integration with AI, consider exploring our related articles:
Learn how BIM is transforming the construction landscape: What is Building Information Modeling (BIM) and How it is Shaping the Construction Industry
Conserve Energy Future – Green Building: A comprehensive resource for everything related to green building and sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, green building construction is a cutting-edge technology and revolutionizing the construction industry. By focusing on sustainability, energy efficiency, and human well-being, green buildings are not just a trend but a necessity in a world seeking a greener and more sustainable future.